
Certificate management under Android
To access pages with a Browser (e. g. Chrome) under Android that require "client authentication" with a certificate, a corresponding certificate must be imported. In the example the URL "https://vc.edv-workshops.com" is to be accessed (the address does not exist).
If you have not imported a certificate, the error message "400 Bad Request - No required SSL certificate was sent" or "403 Forbidden" will appear when the address is accessed.
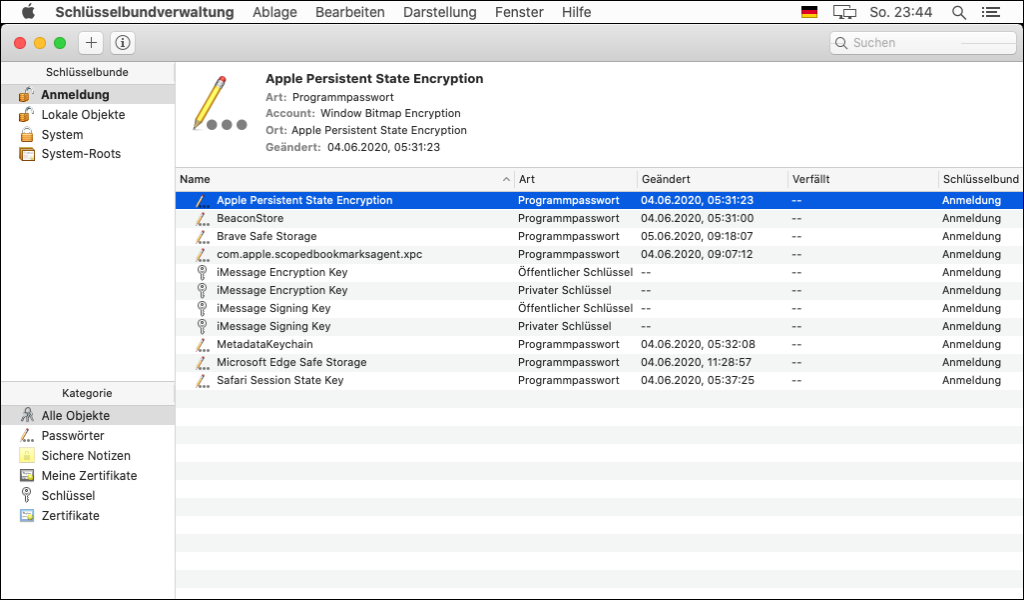
Certificate management under macOS - Keychain
![]() Under Apple macOS, certificates (and other security-relevant information such as logon dates) are stored and managed in a so-called "keychain".
Under Apple macOS, certificates (and other security-relevant information such as logon dates) are stored and managed in a so-called "keychain".
The application can be synchronized with the other Apple devices via the iCloud account, so that a certificate only needs to be installed once on the Apple operating systems (iOS, iPadOS, macOS) and then synchronizes with the other devices (see also Setting up the iCloud keychain).
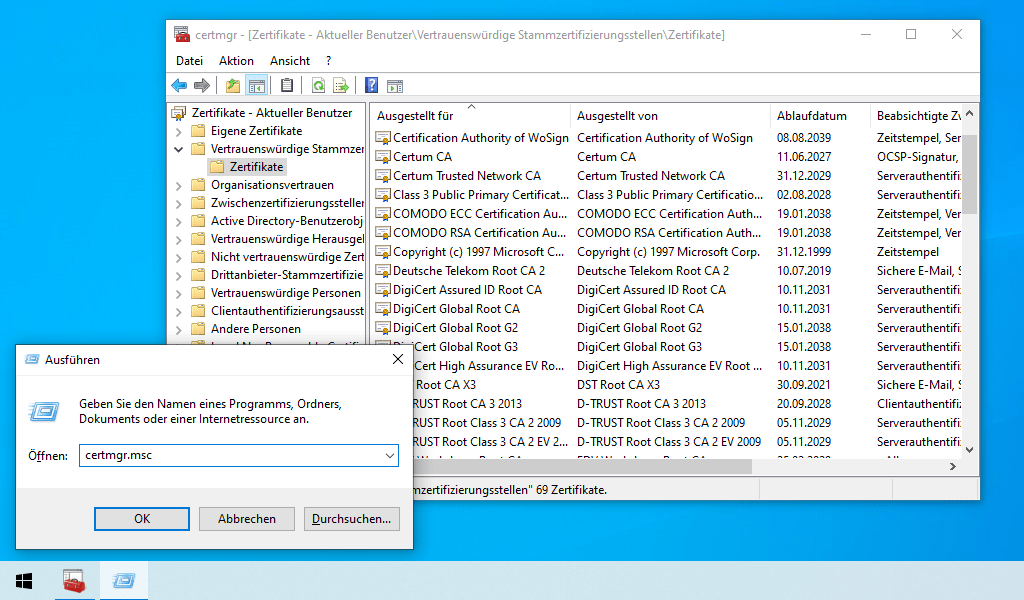
Certificate management under Windows
 Certificates enable you to communicate in encrypted form or to identify yourself (authenticate). Among other things, certificates come in the form of a file with the file extension crt, cert, pem, pf7, p12, pfx, der, p7b or p7c.
Certificates enable you to communicate in encrypted form or to identify yourself (authenticate). Among other things, certificates come in the form of a file with the file extension crt, cert, pem, pf7, p12, pfx, der, p7b or p7c.
In this example, a p12 and a crt file are considered.
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Trusted Root Certificate Program
Microsoft provides a list of trusted root certificates with its products. For this purpose, Microsoft has set up the "Microsoft Trusted Root Certificate Program“.
The Microsoft Root Certificate Program supports the distribution of root certificates so that customers can trust Windows products. The list of trusted root certificates is stored in the certificate store and is constantly updated with Windows Updates.
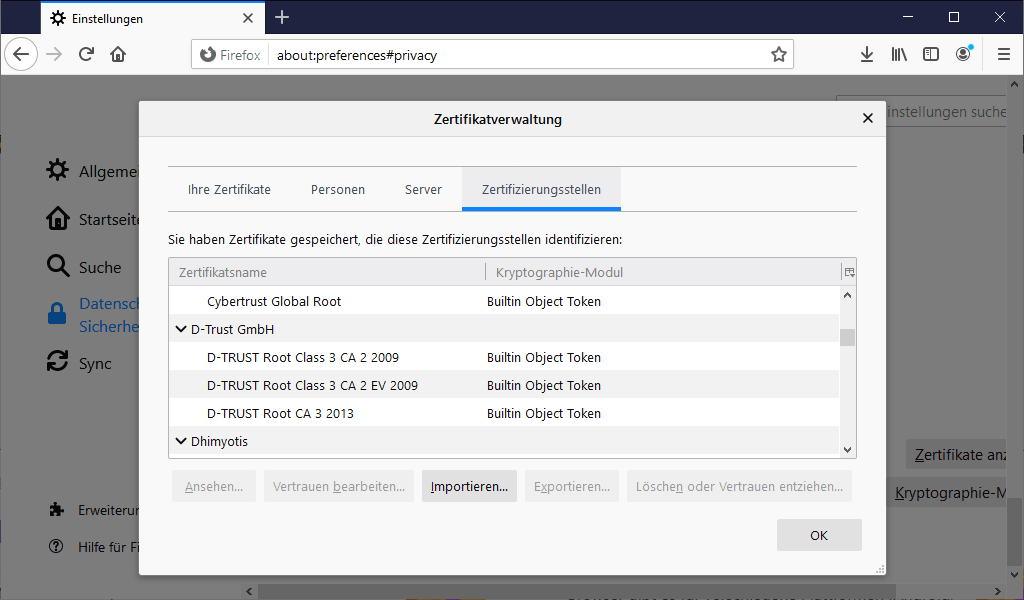
Mozilla Firefox
Selecting the certificate store
Mozilla Firefox comes with its own certificate management, so certificates usually have to be imported into its own certificate store. However, from version 49 (March 2017) Firefox can also be switched to use the Windows certificate store.
This article shows how to switch from Firefox certificate management to Windows certificate management and that protection programs (e.g. Kaspersky Internet Security) could also influence this.
Read more: Mozilla Firefox - Selecting the certificate store
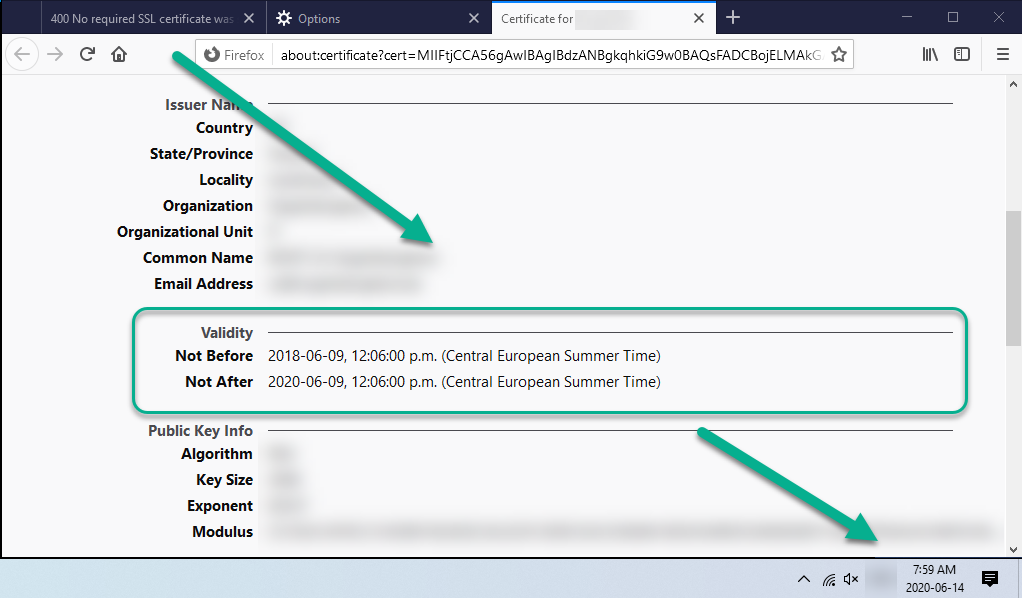
Expired certificate
Observe validity of certificates
If unusual error messages occur during authentication with client certificates, please check the validity of your certificate. In the example, the message "400 Bad Request - No required SSL certificate was sent" appeared because the end of the validity of the certificate had been reached.
Solution: Request a new certificate from your service provider.
 Deutsch (Deutschland)
Deutsch (Deutschland)  English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom)